PACE
About the project
PACE is an algorithm/tool that estimates the anaerobic energy reserve/capacity/balance (W’, pronounced “W prime”) of the body during exercise. It quantifies the capacity of an athlete to produce high-intensity effort, often the performance-limiting or -determining factor in races. In cycling, a relatively controlled environment, the measurement of a rider’s power output allows to calculate a real-time estimate of W’ during exercise.
PACE integrates data measured during exercise and computes a real-time estimate of a rider’s actual W’, based on that athlete’s physiological profile (determined in performance testing). This provices athlete’s performing exercise with real-time feedback on their anaerobic balance and allows them to make decisions and adjust their tactics accordingly.
Applications
- Quantify exertion levels for immediate tactical decisions on pacing strategy.
- Provide pacing plans
- For short, high-intensity events, to maximize performance, i.e., ensure the anaerobic capacity is fully depleted at the end.
- For endurance events, to increase the likelihood of finishing
- Design individualized and efficient training sessions, leading to performance gains and improved health, with main relevant benefit depending on the user group.
For further information about the PACE project, unrelated to the technical development, see to the Victoris project page.
Terminology
Critical Power (CP): The maximum power output that an athlete can maintain over an extended duration (~30–60 min). Physiologically, it corresponds to the highest steady-state oxidative metabolism rate, where lactate production and clearance remain balanced.
Anaerobic Capacity (W’): The finite amount of work that can be exerted above CP before exhaustion. Once W’ is depleted, power output must drop to or below CP to allow (partial) recovery.
IDLab role
IDLab’s tasks within the PACE project include:
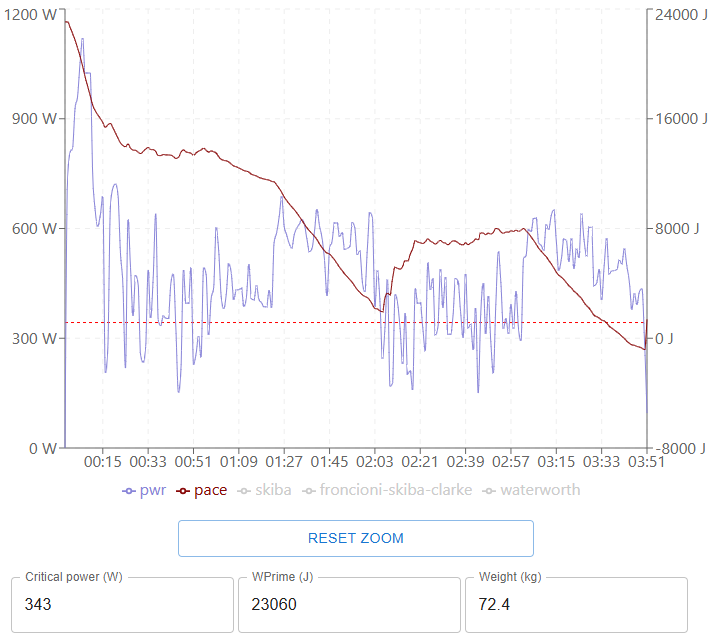
- Visualizing the PACE algorithm in a user-friendly dashboard for post-event data-analysis by coaches or athletes (example below).
- Implementing and presenting the real-time W’ estimation using power data (ANT+ or Bluetooth) and athlete profiles. Initially, a web-app was created to communicate with the power sensor via Bluetooth using Google’s Web Bluetooth API. Further steps include the development of a dedicated mobile application.
Integration with cycling computers and sports watches is not currently pursued due to following limitations:
- The algorithm’s high computational demands relative to these devices’ capacities.
- Limited internet communication capabilities of most such devices, making interfacing with the server running the PACE algorithm not feasible.
An example of a post-analysis visualization: